A cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes is haploid. The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid.
![]()
Homologous Chromosome High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
14 What is homozygous class12.

. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. Up to 24 cash back A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. The 23rd pair the sex chromosomes differ between males and femalesJun 1 2021.
17 What causes homozygosity. What is homozygous psychology. Pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous.
Locus is position on chromosome wh. Homologous chromosomes are pair of chromosomes obtained from each parent male and female. 16 Why is homozygosity a problem.
These chromosome pairs can have homozygous or heterozygous alleles is called. A parent who is homozygous dominant for brown eyes will have brown-eyed children. Homozygous means that the loci in the corresponding chromosomes have the identical alleles.
23 How do you tell if a parent is homozygous. The chromosomes in each pair of chromosomes are called. A homozygous organism is discovered to have either a pair of dominant alleles eg.
Up to 24 cash back A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid. A cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes is haploid.
AA or a pair of recessive alleles for a particular trait eg. One member of each homologous chromosome pair comes from each gene. Gene Allele Locus Homozygous Genotype Heterozygous Phenotype Answer Bank location on a chromosome is a codes for a two different copies are two identical copies are a variation is an makes up.
- 3642552 swaggergirl722 swaggergirl722 05042017 Biology High School answered. The corresponding pair of chromosomes may homozygous as well as heterozygous depending on the presence of dominant and recessive genes. If an organisms haploid number is 6 its diploid number is 3.
It indicates that the alleles have the same characteristic coded for them. What is an example of a genotype of a homozygous pair of. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous.
View the full answer. PHASES Crossing over occurs between tetrads. If an organisms haploid number is 6 its diploid number is 3.
If an organisms haploid number is 6 its diploid number is 3. Alleles are alternate form of genes. 19 What genotype is purebred.
One member of each homologous chromosome pair comes from each gene. A cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes is haploid. The genes are similar in homologous chromosomes.
True or False If an organisms haploid number is 6 its diploid number is -3-. The alleles on the homologous chromosomes may be different resulting in different phenotypes of the same genes. 22 Is BB heterozygous or homozygous.
One form is designated as dominant and the other as recessive. One member of each homologous chromosome pair comes from each gene. One of the sets comes from the mother and the other set from the father.
In homozygous animals these alleles are identical. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 20 Is KK a genotype.
External ophthalmoplegia with rib and vertebral anomalies EORVA is characterized by congenital nonprogressive external ophthalmoplegia ptosis scoliosis torticollis vertebral and rib anomalies caused by homozygous mutations in the myogenic factor 5 gene MYF5 located on chromosome 12q2131Uniparental disomy UPD is a rare inheritance of a. One member of each homologous chromosome pair comes from each gene. The term homozygous is used to describe that which has the same or identical alleles for a particular trait located at similar loci on paired chromosomes ie.
Each genetic trait can be located at a particular site or locus on a chromosome and in a pair of homologous chromosomes there will be two copies of the alleles which code for a particular trait. Match each relationship with the corresponding pair of concepts. One member of each homologous chromosome pair comes from each gene.
A cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes is haploid. One member of each homologous chromosome pair comes from each gene. 21 Is HH purebred.
The corresponding pair of chromosomes may homozygous as well as heterozygous depending on the presence of dominant and recessive genes. 13 How many chromosomes do humans have. The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid.
If an organisms haploid number is 6 its diploid number is 3. If an organisms haploid number is 6 its diploid number is 3. A cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes is haploid.
The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous. 18 What is meant by an allele.
A cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes is. If an organisms haploid number is 6 its diploid number is 3. One member of each homologous chromosome pair comes from each gene.
One member of each homologous chromosome pair comes from. PHASES Each replicated chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosome. During tetrad formation alleles can be exchanged.
The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid. The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid. A cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes is haploid.
Homologous chromosomes are made up of chromosome pairs of approximately the same length centromere position and staining pattern for genes with the same corresponding loci. Answer 1 of 2. This is a pair of chromosomes having the same genes at the same loci.
Twenty-two of these pairs called autosomes look the same in both males and females. In a diploid organism there are two sets of chromosomes. A pair of corresponding chromosomes is homozygous.
Each replicated chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosome forming a tetrad. PHASES Paired homologous chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. 15 Whats a DNA molecule.
The gametes of sexually reproducing organisms are haploid. Possessing identical forms of a gene ie identical alleles at a given genetic locus on each of a pair of homologous chromosomes.
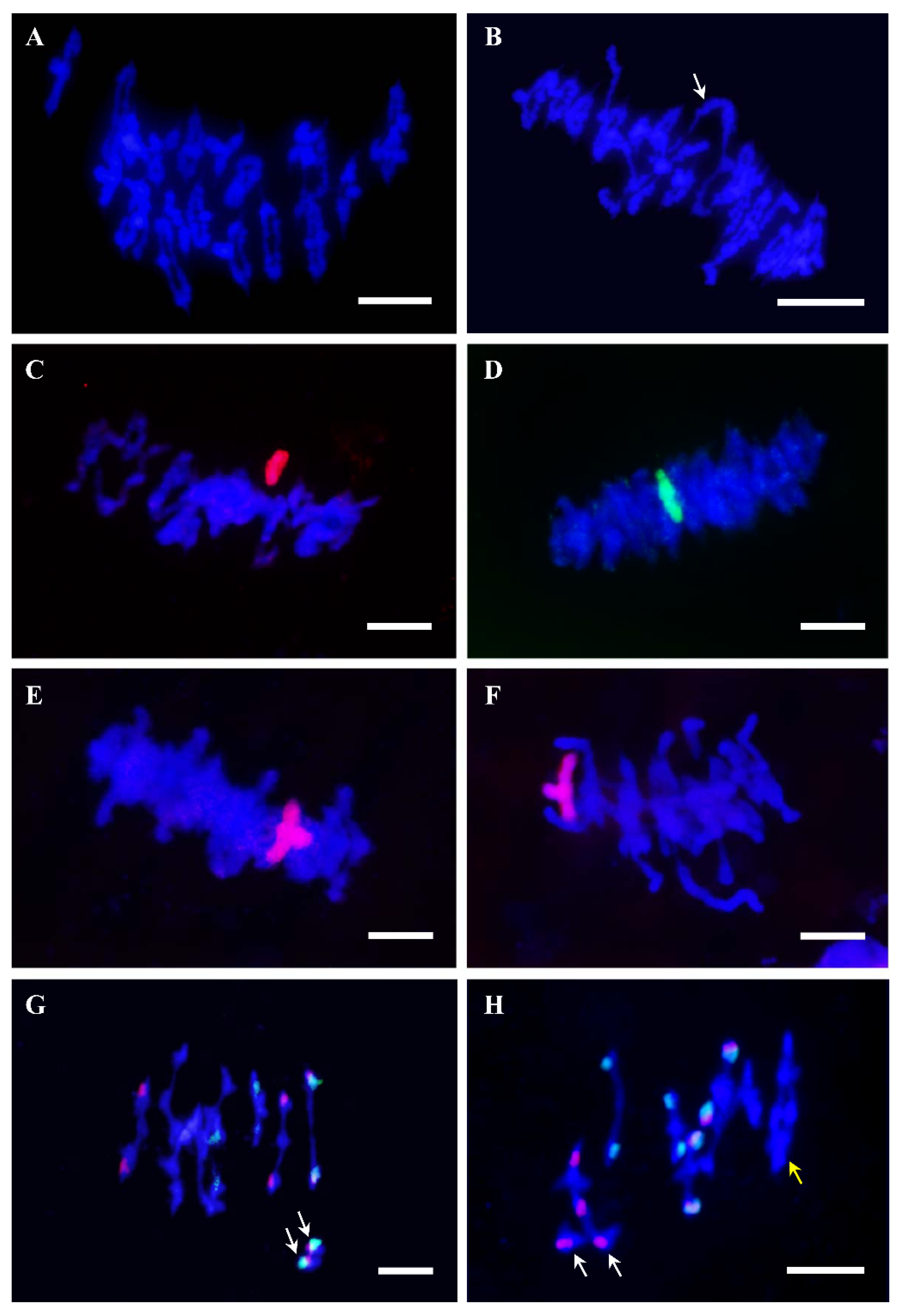
Plants Free Full Text Genomic And Meiotic Changes Accompanying Polyploidization Html

0 Comments